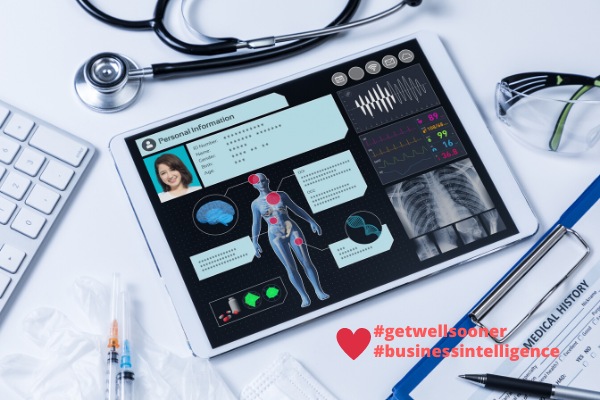
The Internet of medical things goes beyond wearables or analytical systems. It is a whole ecosystem that connects hardware, devices, and sensors, among others, to a network that collects and analyses data in a fast, accurate, and real-time process. It provides health care centers with valuable information to improve patient’s life and business synergies.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming the healthcare industry. IoT-enabled devices and sensors have allowed patients and healthcare providers to monitor vital health parameters in real-time, creating a personalized plan of care for chronic illnesses such as diabetes and heart disease.
This application of advanced technology improves access to care, quality of care, and reduction in the total cost of care.
According to a paper published by Market Research Engine, with a compound annual growth rate of 30% from 2019 to 2025, IoT for healthcare is one of the most important and vital sectors in the technological revolution we are living these days.
The report shows the IoT healthcare market is projected to grow from 41.22 billion USD in 2017 to 265 billion USD by 2025. This growth will be mainly driven by increasing investments in the healthcare market by governments and other stakeholders.
Let’s check the most exciting ways the Internet of Things is transforming healthcare in 2020.
IoT and Healthcare: Remote Patient Monitoring:
This goes far beyond a Fitbit and a smart watch. Although wearable health devices help facilitate healthy habits and bring awareness to a user’s health trends, IoT offers a wide range of wearables and biosensors that provide insight to patterns and correlations crucial to a patient’s health.
Remote monitoring solutions lead to patients receiving treatment and testing in a private, remote environment instead of hospitals and emergency care facilities. This reduces the workload on healthcare workers who are trying to cope with an increased number of patients. Examples of remote monitoring devices include:
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGM)
A CGM is an FDA-approved remote monitoring system that tracks blood sugar levels day and night. It can help detect trends and patterns that give a patient and their doctor a detailed picture of the situation.
A sensor is placed under the skin of your belly or on the back of your arm. It transmits data to a monitor you clip on your belt or an app on your phone. The information can be used to help an individual and their doctor make the best plan for managing diabetes.
Computer Vision
Computer vision is an AI technology that uses algorithms to process images with the intention of making faster and more accurate diagnosis than a physician could make. Computer vision has been used for predicting heart rhythm disorders and estimating blood loss during childbirth.
Telemedicine
As telemedicine becomes more widely used and accepted, insurance companies and government healthcare programs are increasingly stepping up coverage for such care. It helps physicians treat patients who cannot travel easily, those who need to see a doctor promptly or even those who are immunocompromised.
Hospital Operations Management and IoT
As populations and chronic illness continue to increase, it is crucial to improve hospital operations so healthcare professionals can focus on treating patients and not get overwhelmed with paperwork and lagging communication. IoT solutions can automate several operations through a centralized database management system. Here are some ways IoT is improving operations management in hospitals:
RFID Tags
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags or transponders are small devices that use low-power radio waves to receive, store, and transmit data to nearby readers. RFID technology has various uses within the hospital setting. RFID enables more accurate inventory tracking for medicine and pharmaceuticals, patient and staff tracking, and tool tracking in the surgical setting. The application of RFID tags enables hospitals to streamline time-consuming processes and improve communication.
Connected Imaging and Electronic Health Records
You will be hard pressed to find a medical facility that has not transitioned to electronic health records (EHR) and connected imaging. An AMA study found that for every hour of face-to-face time with patients, physicians spend nearly two additional hours on clerical tasks. IoT has transformed the way patient information is managed from the time it is collected to when it is processed and shared within a facility or to other locations.
Connected imaging has enabled radiologists to receive and read scans wherever and share them with other physicians. This allows process time to be much faster without missing out on important features. This means the patient is more likely to get a first-time right diagnosis and a personalized treatment regimen.
IoT When We Need It Most in Health Care
IoT has proven to be quite helpful in the current Covid-19 global pandemic. IoT has enabled prediction and monitoring mapping informing experts, officials and the public of the outbreak situation as it unfolds.
Due to the highly contagious nature of the virus, medical professionals have relied on telemedicine and robots to interact with patients who may be infected. Not only does this reduce the spread of the virus within the medical facility, but with other humans the infected patient may come into contact while traveling to the facility.
Additionally, Portable Lab-On-Chip detection kits will be used to identify infected individuals for proper medical care. Rather than needing a large amount of virus for detection and waiting days for results, this technology can detect, differentiate and identify all 3 coronaviruses in a single test in about 2 hours.
The IoT healthcare market is reshaping healthcare services in the community and around the world. Knowing how it will impact you, your health and your business will prepare you for the future and allow you to focus on what you do best.